
Blazed holographic gratings have similar properties. Classical ruled gratings usually peak with very high efficiency at a certain wavelength and become rapidly less efficient upon deviation from that wavelength.

Various types of diffraction gratings have different efficiencies versus wavelength characteristics. Figure 4: Diagram depicting overlap of the spectral orders.
#Hydrogen bohr model free
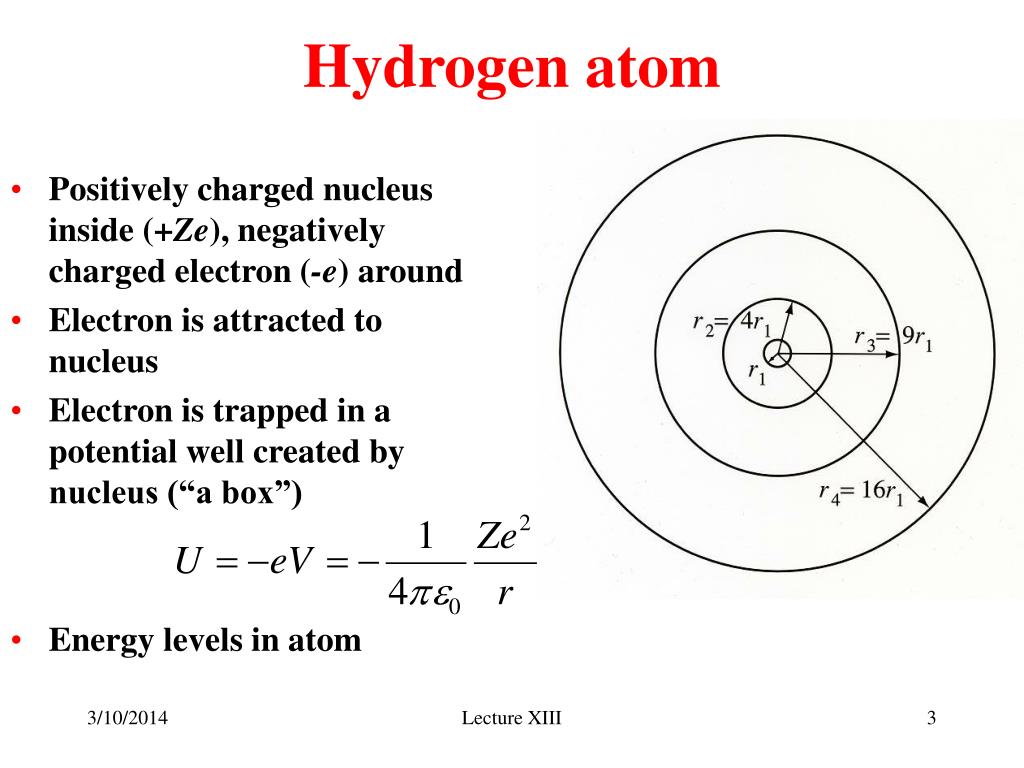
However, since ℓ1 < ℓ2, the free spectral range is equal to the shortest wavelength in the allowed bandwidth divided by the order number: That is, ℓ 2 − ℓ 1 ≤ ℓ 1/m. When ℓ 1 in order m coincides with ℓ 2 order m-1. Conversely, overlap will occur at the short wavelength end If, as shown in Figure 3, ℓ 1 and ℓ 2 are the extremes of the spectrum band, then overlap will occur at the long wavelength end of the spectrum when ℓ 2 in order m is diffracted at the same angle as in order m+1. The free spectral range of a diffraction grating is defined as the largest bandwidth in a given order that does not overlap the same bandwidth in an adjacent order. Consequently a coarse grating (with large d) produces many orders, whereas a fine grating may produce only one or two. The number of orders that can be produced by a given grating is limited by the grating constant d, because it cannot exceed 90 degrees. This type of device (i.e., a beamsplitter) can be used for the generation of multiple lasers. However, if monochromatic light is incident on the grating, several output beams are generated. Each spectrum is composed of monochromatic images of the incident bundle, with the blue image nearer to the central axis. Since light of different wavelengths are diffracted at different angles, each order is drawn out into a spectrum. Only when the resolution is smaller than the difference between the two lines can they be distinguished if resolution is larger, the two lines will not be distinguishable.įor example: Calculate the resolution of a grating system employing a 1200 groove/mm grating (period = d = 0.833 µm), 200 mm focal length imaging mirror, and operating in the first order, with 25 µm slit. In spectral analysis, the resolution is a measure of the ability of the instrument to separate two spectral lines that are close together. The coulombic force is balanced by the centrifugal force, hence: Instead of the gravitational force, in the atom there is an electrostatic force, but the centrifugal force is just the same. Just as the planets move around the sun in stable orbits with centrifugal force just enough to overcome the gravitational forces of attraction, the electrons move around the nucleus. The Bohr model can be viewed as a planetary model. Only orbits for which the angular momentum has integer multiples of h/2π are allowed. The angular momentum of the electron in each of the stable orbits is quantized.In any of these states the electron moves in a circular motion around the nucleus.The energy (hν) of this light equals theĭifference between the energies of the two states.
When it moves from a state of higher energy to one of lower energy, it emits a quantum of light.
#Hydrogen bohr model how to
How to incorporate this new viewpoint of the atom and the quantization condition of Max Planck into a successful theory of the hydrogen atom. Bohr was working in Rutherford’s laboratory at the time and saw Physicist Ernest Rutherford had proposed the nuclear model of the atom based upon the α-particle scattering experiments of his colleagues Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden. The theoretical explanation of the atomic spectrum of hydrogen came from a young Dane named Niels Bohr. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom and, can be modeled using relatively simple physical considerations. He was awarded by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934. Of deuterium ( 2H) and protium ( 1H, hydrogen with no neutrons) will be determined by comparing the spectra of these different hydrogen isotopes. In this experiment, part of this spectrum will be determined. Since the hydrogen atom has only one orbital electron surrounding a nucleus consisting of a single proton, it has a particularly simple atomic spectrum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
